What is recycling?
Recycling, a process of transformation of materials arising from the use of products, consists of the reprocessing of matter, generating a chemical, chemical-physical or even biological transformation. It is different from the principle of reuse, which is related to the attribution of new use to a material that would be discarded, not necessarily subjecting it to some transformation process. Both processes are directly related to sustainability since they enable the reduction of pollutant emissions and the use of energy to manufacture materials, deforestation and damage to the soil. Besides, there is also a decrease in the production of waste and, consequently, in the pollution of the environment.

Waste separation is the first step towards recycling
How does the recycling process work?
Each type of recyclable material requires specific treatment. But the process is constituted as follows: separation, collection, compaction, decontamination/cleaning, and chemical-physical transformation, not necessarily in that order. The main types of materials that can be recycled are paper, plastics, cardboard, glass, metals, fabrics and electronic components.
But then, what are the problems with recycling?
You might be asking yourself this question now: If recycling can bring so many benefits, then what would be the problems with this process?
Well, to answer that question, you first need to understand some concepts. The main one is: 'When we throw something away, we are not solving the problem. For planet Earth, there is no ‘outside’. The waste is just shifting.

With that in mind, it is necessary to reflect on what recycling is. And the very name of the process shows us: the problem is not solved, because, with recycling, the material does not 'disappear' from nature, it remains in our midst but a new format. And yet, these materials never stop being produced. Even though it is reduced, the volume of this waste is always increasing exponentially.
In addition to this problem, we can point out others:
It is not widespread
The table below shows the volume of only plastic waste produced worldwide each year, and how countries deal with it:
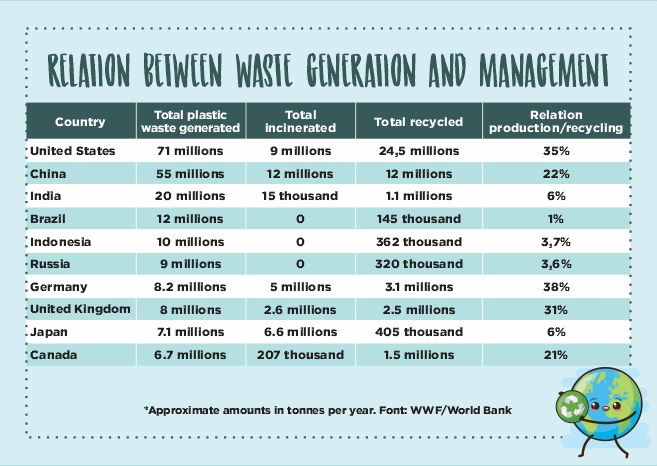
These values are plastic only. This material represents only half of all waste produced in the world according to the World Water Forum and is one of the most resistant and durable materials. On our e-books, you can find much more information about the plastic problem.
Want a free ebook about waste problems and solutions? Just enter your email address for free access!
Needs separation and decontamination
The recycling process, since it is done differently for each material, needs a rigid separation and decontamination process. For this, it is necessary to wash the materials before disposal and also selective collection, something that is implemented very rarely. In Brazil, for example, only 17% of the population has access to this type of process.

Generates costs
Because it is not widely offered, the selective collection – essential for the implementation of the recycling culture – often needs to be contracted separately, which has an additional logistical cost. In addition to the costs related to sorting in recycling centres, which need labour to separate and decontaminate waste; costs that can simply be avoided when using the traditional waste treatment network, which results in the institutions’ lack of interest in overpaying for it.
Waste Management, in general, is already deficient
Waste management, especially in the poorest and emerging countries, is still very precarious. Urban solid waste is often not collected as necessary in the poorest and most peripheral regions, and as a result, many irregular landfills are created and discharged into rivers and streams. Also, many organizations, especially those in the health field, make irregular waste discharges that should have specialized treatment. Therefore, it is very difficult to implement a culture of recycling and selective collection in communities that do not even have access to a basic waste management system.
Does this mean that recycling should not be done?
No way. Recycling, even if it doesn’t solve the garbage problem, provides many benefits. And what are the advantages of recycling?
- Reduces deforestation – caused by the production of paper, cardboard and others – and consequently erosion, silting of rivers, and damage to biomes in general;
- Reduction of gas emissions such as methane;
- Generates jobs – in waste collection and recovery processes
- Generates income – by selling valued materials and selling recycling credits;
- Increases the life cycle of materials and maximizes the value extracted from raw materials;
- Decrease in the amount of garbage in landfills;
- Decreased contamination of streams, rivers and lakes.

Therefore, we must use recycling as one of the factors that will help to preserve the environment and reduce the waste we produce. However, it must be combined with other actions, such as reusing materials, reducing consumption and technologies that solve the problem of waste, such as pyrolysis, for example, which is an environmentally friendly waste treatment technology, with no emissions, zero landfills and with the potential to output energy. Find out more here.
Follow our page on LinkedIn and interact with us.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
We hope you like this post! See you soon! 😉

No responses yet