Carbonization
Technology Description (Abstract)
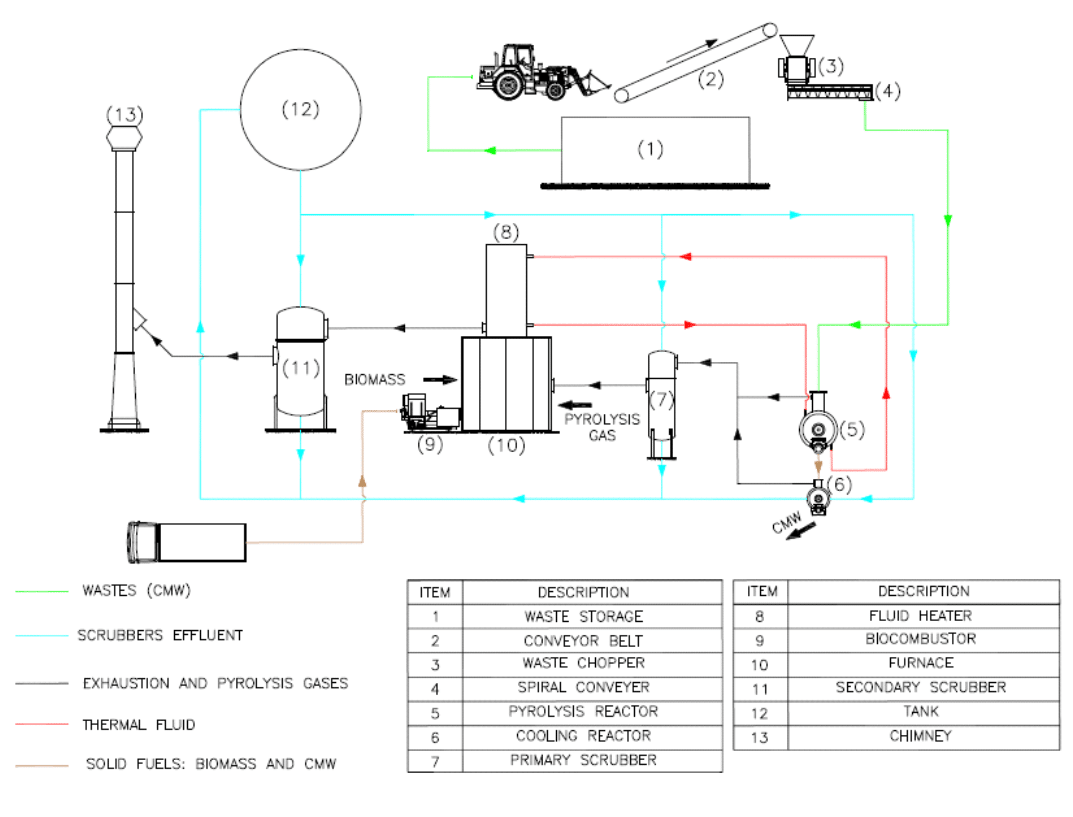
Pyrolix technology is a pyrolysis process carried out in intermittent flow reactors heated by closed-loop thermal fluid in a temperature range of 300 – 330 °C. It is a protected technology, with ownership rights belonging to the Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG) and partner institutions.
Depending on its properties, it is necessary to process waste in a chopper. The process begins with solid waste being loaded to the system through a conveyor belt to the pyrolysis reactor, which is subjected to indirect heating by thermal fluid. In this initial phase, the process is endothermic, and the energy for heating the thermal fluid is provided by burning biomass (wood chips) in the furnace. Exhaustion gases from the furnace are treated in the secondary scrubber. Alkali solution, stored in the tank, is used on both scrubbers, and also to cool the carbonized waste.
When reactor reaches a certain temperature (approximately 200 °C), pyrolysis reactions begin. These reactions generate heat, which is eventually sufficient for maintaining the process running. In the same way, the gases and vapors generated in the reactor are also used in the furnace as fuel to provide heat to thermal fluid, after treatment in the primary scrubber.
The thermal fluid operates in closed circuit, passing through the reactor and the fluid heater, which maintains the temperature in a suitable level for the process (over 300 °C on the thermal fluid and over 850 °C on the furnace). The carbonized waste is discharged on the cooling reactor with temperatures below 60 °C. Production cycles considering loading, processing and discharging take approximately 2,5 hours.
Important facts:
Electrical Generation
The carbonization it is an endothermic process at the beginning, as it need fuels to start, but it ends as an exothermic process, as it generates fuel – the CWR, Carbonized Waste Residue. Between th heat, gases, and the CWR, there are diferent options for electrical generation: thermal plant, rankine cyccle motor generator, or stirling motor generators. It is the size of the project, caractheristics, type of waste stream, etc, that will determine how the electrical generation will be done.